Culturable on standard microbiological media, as the bacteria must persist in an external environment prior to ingestion by the larvae. Our analyses based on separate loci for the cloning versus culture-based assays reveals shared bacterial taxa, suggesting a portion of the microbiome is culturable. This is in contrast to relative unculturability of the majority of vertically transmitted endosymbionts that have been studied thus far in insects. Using almost the entire 16S rRNA amplicon for taxonomic identification allows for increased accuracy in taxonomic assignment. Additionally, studies have shown that increasing sampling depth is not necessary when microbial communities are distinct. Our taxon rarefaction curves indicate that further sampling is required to fully characterize the dung beetle microbiota, despite that our sampling of the cultured isolates from the digestive system of the 3rd instar larvae captures much of the taxonomic variation seen using molecular approaches. However, on-going studies using next generation sequencing technologies to generate 16S rRNA profiles to increase sampling depth within individuals and additional culturing on a wider diversity of media and conditions will resolve this issue. To our knowledge, only one other ground-dwelling insect has been described as provisioning offspring brood chambers with specific bacterial endosymbionts. Females in the beewolf genus, Philanthus, smear the larval brood chambers with the actinomycete, Candidatus Streptomyces philanthi, which produces antimicrobial compounds to protect the larvae and developing pupae from soil fungi and bacteria. As in the bull-headed dung beetle, the beewolf offspring develop underground in individual brood cells the female creates and provisions with both food and endosymbionts. Upon hatching from the egg, the larva takes up the actinomycete endosymbiont. Prior to pupation, the larva smears the endosymbiont in the cocoon and takes it up after eclosion. In the case of the beewolf, the endosymbionts are beneficial, protecting the developing offspring from fungal and bacterial pathogens. Examining other ground and dung nesting insects may identify additional insect-bacterial mutualisms. A further early responsive transcription regulator gene identified encodes a member of the cold shock domain protein family that harbors two domains, CSD and an RNArecognition motif. In contrast to prokaryotic CSD proteins, eukaryotic proteins containing a CSD may also contain other 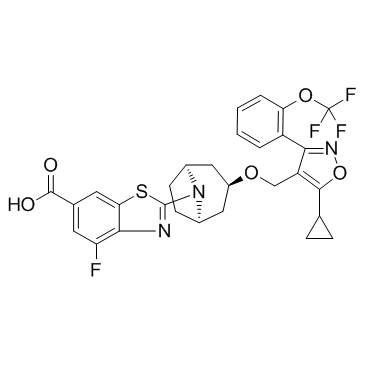 domains and their functions are not exclusively related to cold shock responses. A major cold shock protein in Arabidopsis thaliana, CsdP1, which contains a CSD domain, has been shown to exhibit RNA chaperone activity. In our experiment, expression of the Csd gene was up-regulated within one hour after the HC-toLC shift and started to decrease after two hours. It may therefore be hypothesized that the proposed RNA chaperone function of Csd is important during the initial phase of the CO2 concentration shift to favor translation of newly formed Lomitapide Mesylate transcripts. The MYB-related TF early induced under LC condition contains a single MYB DNA-binding domain. Its transcript abundance was previously reported to increase upon CO2 deprivation, but the biological function of the encoded TF has not yet been characterized. In C. reinhardtii, the MYB domain-containing transcription factor Psr1, a member of the G2-like TF family, regulates phosphate uptake. Mutants lacking a functional Psr1 gene are impaired in the proper acclimation of the cells to phosphorus deficiency. Our data also revealed up-regulation of Hsf1, a member of the heat shock transcription factor family. C. reinhardtii has two Sipeimine annotated HSF genes, while A. thaliana has at least 21 genes.
domains and their functions are not exclusively related to cold shock responses. A major cold shock protein in Arabidopsis thaliana, CsdP1, which contains a CSD domain, has been shown to exhibit RNA chaperone activity. In our experiment, expression of the Csd gene was up-regulated within one hour after the HC-toLC shift and started to decrease after two hours. It may therefore be hypothesized that the proposed RNA chaperone function of Csd is important during the initial phase of the CO2 concentration shift to favor translation of newly formed Lomitapide Mesylate transcripts. The MYB-related TF early induced under LC condition contains a single MYB DNA-binding domain. Its transcript abundance was previously reported to increase upon CO2 deprivation, but the biological function of the encoded TF has not yet been characterized. In C. reinhardtii, the MYB domain-containing transcription factor Psr1, a member of the G2-like TF family, regulates phosphate uptake. Mutants lacking a functional Psr1 gene are impaired in the proper acclimation of the cells to phosphorus deficiency. Our data also revealed up-regulation of Hsf1, a member of the heat shock transcription factor family. C. reinhardtii has two Sipeimine annotated HSF genes, while A. thaliana has at least 21 genes.