We investigated samples of biological interest for which the relative abundance of cell types was unknown. Deconvolution was performed on microarray expression data from white blood cell samples from 72 SLE patients and 45 healthy donors. Proportions of cells of each type and state were calculated. Residuals from fitting the model were relatively low, with a median of 0.11. Stability of the fits was analyzed by repeating the fitting process with each of various cell types omitted ; we Folinic acid calcium salt pentahydrate observed that there was only a very small disturbance in the results of the fit by the remaining cells. Furthermore, the disturbance that did occur was confined to cells that were very similar to the one that was omitted. We tested these results�� validity by comparing them to counts of total lymphocytes, total monocytes, and neutrophils determined by CBC differentials performed on the same blood samples. The correlations between the two methods were reasonably good and very consistent between different cell types. To specifically validate findings of particular interest from deconvolution, we purified and quantified activated NK and T helper cells from SLE patients and healthy controls and tested their level of activation using the conventional method of FACS. Purified NK cells were stained with the classical activation marker CD62L. Consistent with results from deconvolution, two out of three patients showed substantial activation of NK cells compared to healthy donors, while one patient showed mildly elevated levels of NK cell activation. CD4+ T helper cells purified and stained for the marker of naive T cells CD62L show significant down-regulation, indicating activation and suggesting a transition to a memory phenotype. To validate our unexpected 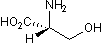 finding that B cells were not activated in lupus patients we purified B cells from the same three patients and quantified levels of CD80, a molecule found on the surface of activated B cells that provides a costimulatory signal for T cell activation. Two of the three patients�� B cells possessed increased levels of CD80. To reconcile this observation with the lack of B cell activation in the main SLE cohort we examined CD80 levels in the expression profiles of the reference resting and activated B cell samples used for deconvolution and found no significant difference between the two groups. Microarray deconvolution is an emerging method for measuring proportions of cell types or states in complex systems. The studies reported here are the first application of this technique to human biology, the first application to blood, and the first application to study immune disease. The autoimmune disease SLE is a prime example of a disease where determining the proportions of immune cells is an Chlorhexidine hydrochloride important contribution to understanding the etiology of the disease. In addition to the biological advances, this study extends previous work on deconvolution in several technical ways that are necessary to support its application to SLE. First, we validate the method using complex biological samples of known composition in order to show that it can be performed on blood samples. Second, we measure the performance of the method on a controlled system with a precisely known answer. Third, we expand the number of component cell types quantified in mixed samples, and we validate the method on an independent test set of those cell types. Here we find that patients suffering from SLE have some types of blood cells activated predominantly: NK cells have the highest activation, followed by T helper cells, monocytes, and dendritic cells.
finding that B cells were not activated in lupus patients we purified B cells from the same three patients and quantified levels of CD80, a molecule found on the surface of activated B cells that provides a costimulatory signal for T cell activation. Two of the three patients�� B cells possessed increased levels of CD80. To reconcile this observation with the lack of B cell activation in the main SLE cohort we examined CD80 levels in the expression profiles of the reference resting and activated B cell samples used for deconvolution and found no significant difference between the two groups. Microarray deconvolution is an emerging method for measuring proportions of cell types or states in complex systems. The studies reported here are the first application of this technique to human biology, the first application to blood, and the first application to study immune disease. The autoimmune disease SLE is a prime example of a disease where determining the proportions of immune cells is an Chlorhexidine hydrochloride important contribution to understanding the etiology of the disease. In addition to the biological advances, this study extends previous work on deconvolution in several technical ways that are necessary to support its application to SLE. First, we validate the method using complex biological samples of known composition in order to show that it can be performed on blood samples. Second, we measure the performance of the method on a controlled system with a precisely known answer. Third, we expand the number of component cell types quantified in mixed samples, and we validate the method on an independent test set of those cell types. Here we find that patients suffering from SLE have some types of blood cells activated predominantly: NK cells have the highest activation, followed by T helper cells, monocytes, and dendritic cells.