Indicating that Necl-4 does not play an essential role for developmental myelination in the PNS as well. Expression analyses did not support the idea of functional compensation by other Necl proteins, because Necl-4 is the only Necl protein whose expression is upregulated in myelinating oligodendrocytes, and disruption of Necl4 did not significantly change the expression level of other Necl proteins in the CNS and the 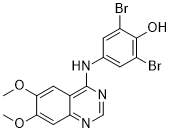 PNS. One plausible explanation for the discrepancy between in vitro experiments and in vivo observations is that the initiation of axonal myelination may also involve interactions between other cell adhesion molecules such as laminins and integrins and this interaction might be disrupted in dissociate culture and therefore can not compensate for the loss of Necl-1/Necl-4 interaction. Further studies with compound mutants of Necl-4 and other adhesion proteins could delineate the role of various cell adhesion molecules in myelination in the developing nervous system. The threat of an influenza virus pandemic is increasing worldwide, highlighting the need for a diagnostic test kit that can identify the viral strain and its drug resistance. Current methods for identifying influenza virus strains are mainly based on real-time polymerase chain reaction technology or immune-chromatography. RT-PCR technology is highly sensitive and provides genome sequence information, but requires costly instruments. In contrast, immune-chromatography allows rapid visualization of the target virus without the use of instruments, but shows cross reactivity and provides no genomic inAbMole Niflumic acid formation such as human pathogenicity or drug resistance. Thus, molecular tools that selectively recognize and visualize virus genomes without the need for instruments would enable rapid onsite identification of virus pathogens and their drug resistance. Peptide nucleic acids are DNA/RNA analogues in which the phosphate backbone has been replaced by a neutral amide backbone composed of N-glycine linkages. The advantages of PNAs for molecular recognition are their high binding affinity, good mismatch discrimination, nuclease and protease resistance, and low affinity for proteins. These attributes make PNAs particularly useful for detecting viral mRNA in cells. BisPNA-AEEA is composed of two homopyrimidine PNA strands connected via a linker molecule, 2-aminoethoxy-2ethoxy acetic acid. BisPNA-AEEA can invade duplex DNA and form a stable PNA/DNA/PNA triplex with the complementary homopurine strand via Watson-Crick and Hoogsteen base pairing. Modification of cationic peptides on bisPNA further enhanced the triplex formation efficiency of bis-PNA to not only homopurine, but also purine-pyrimidine mixed sequences within duplex DNA. In this study, we prepared a newly synthesized bisPNA-AZO which contains an azobenzene amino acid linker instead of the AEEA linker of bisPNA-AEEA. Liang et al. reported that an oligonucleotide tethered to a trans-azobenzene intercalates between base pairs and stabilizes the duplex by stacking interactions.
PNS. One plausible explanation for the discrepancy between in vitro experiments and in vivo observations is that the initiation of axonal myelination may also involve interactions between other cell adhesion molecules such as laminins and integrins and this interaction might be disrupted in dissociate culture and therefore can not compensate for the loss of Necl-1/Necl-4 interaction. Further studies with compound mutants of Necl-4 and other adhesion proteins could delineate the role of various cell adhesion molecules in myelination in the developing nervous system. The threat of an influenza virus pandemic is increasing worldwide, highlighting the need for a diagnostic test kit that can identify the viral strain and its drug resistance. Current methods for identifying influenza virus strains are mainly based on real-time polymerase chain reaction technology or immune-chromatography. RT-PCR technology is highly sensitive and provides genome sequence information, but requires costly instruments. In contrast, immune-chromatography allows rapid visualization of the target virus without the use of instruments, but shows cross reactivity and provides no genomic inAbMole Niflumic acid formation such as human pathogenicity or drug resistance. Thus, molecular tools that selectively recognize and visualize virus genomes without the need for instruments would enable rapid onsite identification of virus pathogens and their drug resistance. Peptide nucleic acids are DNA/RNA analogues in which the phosphate backbone has been replaced by a neutral amide backbone composed of N-glycine linkages. The advantages of PNAs for molecular recognition are their high binding affinity, good mismatch discrimination, nuclease and protease resistance, and low affinity for proteins. These attributes make PNAs particularly useful for detecting viral mRNA in cells. BisPNA-AEEA is composed of two homopyrimidine PNA strands connected via a linker molecule, 2-aminoethoxy-2ethoxy acetic acid. BisPNA-AEEA can invade duplex DNA and form a stable PNA/DNA/PNA triplex with the complementary homopurine strand via Watson-Crick and Hoogsteen base pairing. Modification of cationic peptides on bisPNA further enhanced the triplex formation efficiency of bis-PNA to not only homopurine, but also purine-pyrimidine mixed sequences within duplex DNA. In this study, we prepared a newly synthesized bisPNA-AZO which contains an azobenzene amino acid linker instead of the AEEA linker of bisPNA-AEEA. Liang et al. reported that an oligonucleotide tethered to a trans-azobenzene intercalates between base pairs and stabilizes the duplex by stacking interactions.
All posts by NaturalProductLibrary
It differed from the conclusion of Bezerra et al in which HAdV was the most common pathogen in coinfection
RSV A was much more common than RSV B. RSV was reported to be responsible for 33.8 million cases of lower ARI in 2005, of which 96% was in developing countries. It would be important for local pediatricians to use antibiotics cautiously when children are hospitalized with ARIs. HRV has been known to be responsible for upper ARIs as well as for some lower respiratory infection in children. Our findings showed the presence of HRV in all age groups. Most HRVs were commonly detected as single infection, which agreed with the report of Bezerra et al. The rest of the cases were co-infections with PIV, RSV. HAdV was another important virus detected as single infection; only one case was detected as co-infection with HRV. HAdV was reported to be responsible for 5�C10% of ARI in children. Our findings confirmed this report, showing a detection rate of 9.6 %, with 11 of the 13 patients infected by HAdV were under six years old. The high detection rate of PIV and CoV in co-infections and multiple infections was an interesting finding. PIV was present in 50% of co-infections. In particular, PIV3 and CoV NL63 were the most common types found. The much higher detection rate of CoV NL63 differed from AbMole Pantoprazole sodium previous epidemiological studies, in which CoV 229E and CoV OC43 were the most common types. It is possible that the other types of CoV were not circulating in the area during the period of study. Meanwhile, the findings suggest that nosocomial infection cannot be ruled out. Although hMPV had low prevalence in this study, only five hMPV infection cases were detected and were all aged between 1 to 6 years, which was in agreement with previous studies. We found that RSV was detected mainly during winter and 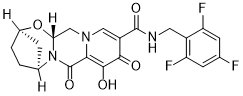 spring, which corresponds with the cold and dry seasons. Typical continental climate with cold and dry winters, and the large difference between the indoor and outdoor temperatures in Gansu Province can easily induce respiratory diseases. A multiple RT-PCR method was used in this study to detect sixteen common respiratory viruses. This method was economical and fast in obtaining pathogen information, and both its sensitivity and specificity have been confirmed. In conclusion, this study provided background information concerning the respiratory viral etiology in Lanzhou area of Gansu Province. Our findings could serve as a reference for local CDC in drawing up further plans to prevent and control ARIs. They will also help clinicians to choose medicines for patients with ARIs. Moreover, the use of multiple RT-PCR makes rapid, effective, and affordable detection for virus a reality in resource limited areas. Multiple myeloma is a hematological cancer characterized by the malignant proliferation of monoclonal plasma cells in the bone marrow. The worldwide incidence of MM has been estimated to be 1.7 men and 1.2 women per 100,000 individuals per year, most prevalent among older adults between the ages of 65 and 70 years. Mortality worldwide is estimated to be 1.1 men and 0.9 women per 100,000 individuals worldwide.
spring, which corresponds with the cold and dry seasons. Typical continental climate with cold and dry winters, and the large difference between the indoor and outdoor temperatures in Gansu Province can easily induce respiratory diseases. A multiple RT-PCR method was used in this study to detect sixteen common respiratory viruses. This method was economical and fast in obtaining pathogen information, and both its sensitivity and specificity have been confirmed. In conclusion, this study provided background information concerning the respiratory viral etiology in Lanzhou area of Gansu Province. Our findings could serve as a reference for local CDC in drawing up further plans to prevent and control ARIs. They will also help clinicians to choose medicines for patients with ARIs. Moreover, the use of multiple RT-PCR makes rapid, effective, and affordable detection for virus a reality in resource limited areas. Multiple myeloma is a hematological cancer characterized by the malignant proliferation of monoclonal plasma cells in the bone marrow. The worldwide incidence of MM has been estimated to be 1.7 men and 1.2 women per 100,000 individuals per year, most prevalent among older adults between the ages of 65 and 70 years. Mortality worldwide is estimated to be 1.1 men and 0.9 women per 100,000 individuals worldwide.
SGA-treated elderly persons and several warnings have also been issued by health agencies
Advising of the increased risk of cerebrovascular events and death in patients with dementia treated with antipsychotic agents. Nevertheless, the practice of prescribing antipsychotics to elderly patients has continued and risperidone, the only SGA with an official indication for behavioural disturbances of dementia in Canada as well as in Europe and the US, remains the antipsychotic agent most commonly prescribed to the over-65 age group. The superiority of SGAs in terms of lower incidence of movement disorders or EPS such as acute dystonia, akathisia, parkinsonism and tardive dyskinesia, has been recently challenged. The current study was designed to evaluate in a real world setting the incidence of movement disorders in the entire population of elderly residents of a Canadian province treated for various diagnoses with either risperidone or an FGA. This study provides data on the incidence of EPS adverse events in the entire elderly population of the Canadian province of Manitoba treated with antipsychotic pharmacotherapy. More than 70% of the population initiated on a SGA was prescribed risperidone. Our results show that the use of FGAs is associated with an increased risk of EPS compared to treatment with risperidone. These results are supported by biological plausibility and are consistent with the findings of previous observational studies.We here provide a structural explanation for the observed switch in oligomerization state of the cortexillin-1 AbMole Dimesna coiled coil from a dimer to a trimer and further generalize the relationship between coiled-coil oligomerizationstate specificity and trigger-sequence function. Our study therefore represents a confirmation and extension of existing sequence-tostructure rules. Such detailed information on coiled-coil sequence-to-structure rules should be beneficial for retrospective interpretation of existing results and could form a basis for design of new molecular entities. A well-documented example is the application of a coiled coilbased strategy for the investigation of the activation mechanisms of prokaryotic and eukaryotic transmembrane receptors. These studies have shown that dimerization is not always sufficient to induce autophosphorylation and that additional conformational changes such as, for example, rotation of the kinase domains relative to each other are required for activation. A coiled-coil based approach has been used to test the dimerization-rotation model for several homodimeric proteins. Typically, the extracellular domain of a given receptor is replaced by the short dimeric coiled coil of the S. cerevisiae transcription factor Put3 and fused to its transmembrane domain and intracellular domain. By removing residues of the transmembrane domain at the junction to the coiled coil, designed variants with seven different rotational conformations of the cytosolic domains relative to each other were generated by imposing the Put3 heptad-repeat pattern. However, in some cases the Put3 coiled coil might not be stable or specific enough to impose the conformations on the transmembrane domain and/or the cytoplasmic domain.
At the e and g positions as well as the packing of these amino acids against
The hydrophobic a and d core residues also contribute significantly to oligomerization-state specificity of coiled coils. This is exemplified by the trimerization motif that specifies a three-stranded, parallel topology of coiled-coil domains. The trimerization driving force of the motif can be explained by optimal side chain�Cside chain interactions whereby the strictly conserved arginine and glutamate residues form a distinct, bifurcated, interhelical salt-bridge network and participate in the formation of the hydrophobic core by establishing tight packing interactions to the neighbouring residues at the a 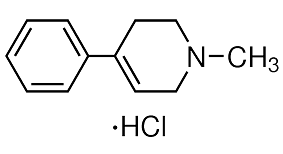 and d positions through their aliphatic moieties. An open issue is that the presence of a specific oligomerizationstate determinant frequently does not correlate with the corresponding coiled-coil topology. Although the trimerization motif RhxxhE is predominantly found in protein families harboring parallel, addition chronic accumulation triggers reduction sst level three-stranded coiled-coil domains, it is also present in some dimers and antiparallel trimers. We have recently addressed this issue and identified a general link between coiledcoil oligomerization-state specificity and trigger-sequence function. By using the archetype coiled-coil domain of the yeast transcriptional activator GCN4 as a model system, we showed that trimer-specific oligomerization-state determinants such as the trimerization motif or isoleucine residues at the heptad-repeat a and d positions switch the peptide’s topology from a dimer to a trimer only when inserted into the trigger sequence. We successfully confirmed our results in two other, unrelated coiledcoil dimers, ATF1 and cortexillin-1. Because of its substantial size of 18 continuous heptad repeats, we used a combination of trimerspecific determinants to switch the cortexillin-1 coiled coil from a dimer to a trimer. Accordingly, we rationally substituted residues to complement two ideal trimerizer motifs of the type R-IxxIE and introduced one additional hydrophobic core isoleucine residue in the trigger sequence of the cortexillin-1 coiled coil. These substitutions were designed to span the entire trigger sequence. Because high-resolution structural information could not be obtained for the full-length Cort-Ir-M1 trimer, the aim of the present study was to perform a detailed structural characterization of two fragments spanning the trigger sequence of the trimeric Cort-Ir-M1 coiled coil using circular dichroism, anatytical ultracentrifugation and x-ray crystallography. We provide the structural basis for the observed switch in oligomerization state of the cortexillin-1 coiled coil from a dimer to a trimer, and therefore provide further evidence for the general link between coiled-coil oligomerization-state specificity and trigger-sequence function. The dissociation constant of GFP-Cort-Ir-M1-short1 was calculated using a two-state-model, assuming only monomeric and trimeric species as there was no experimental evidence for the presence of significant amounts of dimers.
and d positions through their aliphatic moieties. An open issue is that the presence of a specific oligomerizationstate determinant frequently does not correlate with the corresponding coiled-coil topology. Although the trimerization motif RhxxhE is predominantly found in protein families harboring parallel, addition chronic accumulation triggers reduction sst level three-stranded coiled-coil domains, it is also present in some dimers and antiparallel trimers. We have recently addressed this issue and identified a general link between coiledcoil oligomerization-state specificity and trigger-sequence function. By using the archetype coiled-coil domain of the yeast transcriptional activator GCN4 as a model system, we showed that trimer-specific oligomerization-state determinants such as the trimerization motif or isoleucine residues at the heptad-repeat a and d positions switch the peptide’s topology from a dimer to a trimer only when inserted into the trigger sequence. We successfully confirmed our results in two other, unrelated coiledcoil dimers, ATF1 and cortexillin-1. Because of its substantial size of 18 continuous heptad repeats, we used a combination of trimerspecific determinants to switch the cortexillin-1 coiled coil from a dimer to a trimer. Accordingly, we rationally substituted residues to complement two ideal trimerizer motifs of the type R-IxxIE and introduced one additional hydrophobic core isoleucine residue in the trigger sequence of the cortexillin-1 coiled coil. These substitutions were designed to span the entire trigger sequence. Because high-resolution structural information could not be obtained for the full-length Cort-Ir-M1 trimer, the aim of the present study was to perform a detailed structural characterization of two fragments spanning the trigger sequence of the trimeric Cort-Ir-M1 coiled coil using circular dichroism, anatytical ultracentrifugation and x-ray crystallography. We provide the structural basis for the observed switch in oligomerization state of the cortexillin-1 coiled coil from a dimer to a trimer, and therefore provide further evidence for the general link between coiled-coil oligomerization-state specificity and trigger-sequence function. The dissociation constant of GFP-Cort-Ir-M1-short1 was calculated using a two-state-model, assuming only monomeric and trimeric species as there was no experimental evidence for the presence of significant amounts of dimers.
Optimize not only the time of initial application but also the total duration of application
Aside from the dependence on in vitro culture time, cytokines present in vivo can also influence integration. A study examined the effects of steroid hormones in bovine cartilage that is lacking a known inhibitor to integration, interleukin-1b. An increase of,50 kPa in mechanical integration was seen, as compared to the 700 kPa obtained in this study for the native-tonative controls. Also, it has also been shown that, without the assistance of exogenous agents, strength of half that which is seen in intact cartilage can be achieved in an equine model for chondrocyte transplantation. It is worth noting that, in the present study, by delivering cells to the interface in 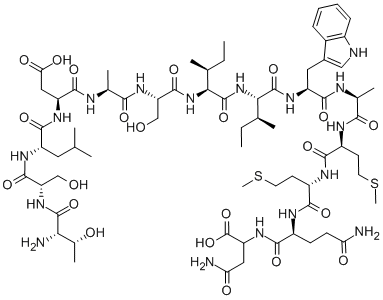 concert with LOX, integration strength can be increased to 1.6 MPa. Comparing this result to the stiffness of fibrin, which is clinically used as tissue glue and sealant, the stiffness of the LOXtreated interface is roughly fifty times higher. Averaged over various strain rates, the stiffness of fibrin alone is under 30 kPa. When fibrin is combined with chondrocytes to serve as a cartilage adhesive, the stiffness of the interface is increased over fibrin alone and also with time in vivo, to 0.645 MPa after 8 months. It is worth noting that LOX-treatment achieves twotimes the stiffness in a fraction of the time. It is expected that the stiffness of interfaces enhanced with LOX and chondrocytes will continue to improve in vivo as the cells remodel the matrix over time. Chondrocyte transplantation is a current therapy that, similar to the self-assembled constructs employed in this study, delivers metabolic cells to the wound edge using fibrin. It is conceivable for LOX to assist this clinical procedure, especially since the LOX treatment produces comparable results to fibrin at a shorter time. Of course, additional studies on 1) optimal dosing time, 2) cross-linker concentration, and 3) activity profile as related to not only the chondrocytes but also other cell types surrounding cartilage would need to be completed to ensure safety and efficacy, prior to deploying this technique clinically. A major component of articular cartilage ECM is the electronegative aggrecan. This electric charge is an obstacle to integration because the similar charges in two pieces of tissue would cause them to repel. Further studies need to be completed to fully understand the role which aggrecan��s electronegativity may play in blocking integration. Future studies might also include the combination of LOX with other bioactive agents that are known to influence cartilage behavior. Already, transforming growth factor b1 has shown efficacy when combined with a biomaterial, and it would be interesting to examine how LOX can assist this case. TFG-b1 may work in synergism with LOX, the cytokine and enzyme working in tandem to effect greater collagen production and cross-linking. It should be mentioned that, for this study, LOX concentration was based on a pilot study that examined LOX on native and engineered cartilages separately. Following this study’s exciting results, it may be prudent to conduct a systematic examination of various LOX concentrations to identify a minimum, yet effective, concentration between 0.015 and 0.15 mg/ml that enhances AbMole Halothane interfacial stiffness and strength to the levels of the engineered or native cartilages, or even for other tissues where cross-linking plays important functional roles. For instance, integrating engineered knee meniscus to native knee meniscus has shown dependence on maturation state, and therefore the extent of collagen crosslinks, and LOX may be used similarly for this tissue. Finding this minimum dose will be significant in not only reducing cost but also in mitigating any potential for this enzyme to interfere with other cellular processes, despite this being a naturally-occurring enzyme.
concert with LOX, integration strength can be increased to 1.6 MPa. Comparing this result to the stiffness of fibrin, which is clinically used as tissue glue and sealant, the stiffness of the LOXtreated interface is roughly fifty times higher. Averaged over various strain rates, the stiffness of fibrin alone is under 30 kPa. When fibrin is combined with chondrocytes to serve as a cartilage adhesive, the stiffness of the interface is increased over fibrin alone and also with time in vivo, to 0.645 MPa after 8 months. It is worth noting that LOX-treatment achieves twotimes the stiffness in a fraction of the time. It is expected that the stiffness of interfaces enhanced with LOX and chondrocytes will continue to improve in vivo as the cells remodel the matrix over time. Chondrocyte transplantation is a current therapy that, similar to the self-assembled constructs employed in this study, delivers metabolic cells to the wound edge using fibrin. It is conceivable for LOX to assist this clinical procedure, especially since the LOX treatment produces comparable results to fibrin at a shorter time. Of course, additional studies on 1) optimal dosing time, 2) cross-linker concentration, and 3) activity profile as related to not only the chondrocytes but also other cell types surrounding cartilage would need to be completed to ensure safety and efficacy, prior to deploying this technique clinically. A major component of articular cartilage ECM is the electronegative aggrecan. This electric charge is an obstacle to integration because the similar charges in two pieces of tissue would cause them to repel. Further studies need to be completed to fully understand the role which aggrecan��s electronegativity may play in blocking integration. Future studies might also include the combination of LOX with other bioactive agents that are known to influence cartilage behavior. Already, transforming growth factor b1 has shown efficacy when combined with a biomaterial, and it would be interesting to examine how LOX can assist this case. TFG-b1 may work in synergism with LOX, the cytokine and enzyme working in tandem to effect greater collagen production and cross-linking. It should be mentioned that, for this study, LOX concentration was based on a pilot study that examined LOX on native and engineered cartilages separately. Following this study’s exciting results, it may be prudent to conduct a systematic examination of various LOX concentrations to identify a minimum, yet effective, concentration between 0.015 and 0.15 mg/ml that enhances AbMole Halothane interfacial stiffness and strength to the levels of the engineered or native cartilages, or even for other tissues where cross-linking plays important functional roles. For instance, integrating engineered knee meniscus to native knee meniscus has shown dependence on maturation state, and therefore the extent of collagen crosslinks, and LOX may be used similarly for this tissue. Finding this minimum dose will be significant in not only reducing cost but also in mitigating any potential for this enzyme to interfere with other cellular processes, despite this being a naturally-occurring enzyme.